What We Do for Detection in the Cloud
Updated on October 25, 2022, by Xcitium
Valkyrie Global Threat Cloud
What We Do for Detection in the Cloud
Xcitium Valkyrie is a cloud-based, verdict-driven platform that provides static, dynamic, and as-needed, expert human analysis for submitted files of unknown and zero-day files. The Valkyrie verdict system analyzes over 200 million file queries per day and more than 300 million unknown files each year through tightly integrated Xcitium solutions and our active global community of threat researchers. This section describes the wide array of techniques used to determine trust verdicts for every file running on the endpoint. 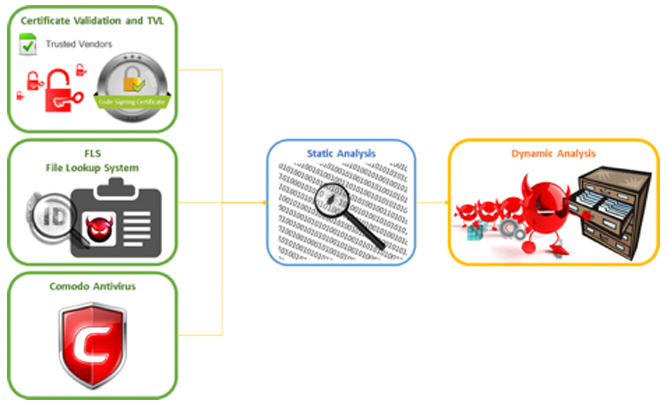
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS: BEHAVIORAL MONITORING
Dynamic analysis detects malicious files that might be unrecognized by legacy techniques. Dynamic analysis runs and monitors the behaviors of a file to catch malicious files that cannot be detected by static analysis methods. Dynamic analysis takes longer than static analysis but it is a critical part of detection. Automatic dynamic analysis is done by inspecting the run-time behavior of a file such as if it is attempting to create, delete or modify files, registry values, processes, memory locations or other specific operating system entities and network connections.
Dynamic analysis can be applied to different file types such 32/64 bit executable Windows files, pdf files, Office documents and html files that include executable scripts and stand-alone script files, e.g.bat,py,s. Xcitium Valkyrie sandbox dynamic analysis is performed on the submitted PE file. Automatic dynamic analysis includes both behavioral and environmental analysis of unknown files exhibiting any of the following: ‘anti-VM’ evasion, VM escape attempts, sleep commands intended to wait out analysis, system modifications to the registry, file system pollution, system API calls and returns, and many more techniques that contribute to determine a trust verdict (a file is either good or bad, no assumptions).
Static Analysis: 26+ Static Detectors
Automatic static analysis allows detection of malicious files that might not be recognized by legacy techniques such as antivirus engines and blacklists. For example, malware writers frequently ‘pack’ or compress their malware to obfuscate it and escape analysis. Valkyrie static analysis supports over 450 unpackers ensuring these evasive tactics fail.
Xcitium Valkyrie extracts and analyzes static detector data on submitted PE files and determines a verdict. Static analysis detectors include: binary level analysis, included libraries, system calls embedded in the code, extractable links, unpackers, string analysis and many more detectors that determine a trust verdict. Automatic static analysis is done by using only binary features of the file such as format of the file, format anomalies, and sections in the file, contents of sections, location of sections and section anomalies. Static analysis can be applied to any type of file, such as 32/64 bit executable Windows files, pdf files,
Office documents, html files, and stand-alone script files, e.g. bat, py, js. Static analysis is a fast method and able to process large numbers of files in a shorter time than the behavioral approach of dynamic analysis, but dynamic analysis plays a critical role in catching what static analysis misses.
Expert Human Analysis
Expert human analysis performed by Xcitium Threat Labs, is available with Xcitium solutions that automate integration with the cloud enabled Valkyrie Verdict Driven Platform. On average, the Valkyrie file verdict system provides an accelerated verdict for 83% of all files submitted, in 30 seconds – 3 times faster than competing solutions. However, approximately 17% of submissions cannot receive a verdict through static or dynamic analysis due to software problems and supported file types, as well as malware adapting and evolving new techniques to evade detection and analysis.
This is why Xcitium includes Expert Human Analysis to ensure the industry’s only 100% trust verdict system—where all files receive a trust verdict of good or bad. Complete with Service Level Agreement (SLA), Xcitium is the first and only provider on the market to integrate human intelligence with automatic analysis to convert every unknown file to known.
DYNAMIC MACHINE LEARNING: AI ENGINEERED DETECTION IN THE CLOUD
Xcitium Valkyrie integrates machine learning throughout its automated verdict system. Research and analysis drives the development of ‘big data’ algorithms and methodologies that increase verdict coverage and accuracy. Hundreds of thousands of malicious and clean files are used in training dynamic machine learning models and they are improved with new files regularly. Machine learning training techniques combine algorithms and hundreds of static features extracted from files. Very large sets of malicious and clean files are used in machine learning models and refreshed with new files regularly.
Machine learning-based models ensure high accuracy and reduce the management overhead typically associated with exploit validation and response. Xcitium uses static, dynamic, and broader machine-learning models to detect malware. Static machine learning models know what a clean file should look like. They can detect potential new malware for analysis such as zero-day malicious files that have features that are not explicitly known and are not likely to be detected by legacy methods. In addition, machine learning models trained on specific malware types help improve the accuracy of automatic techniques. Like the static machine learning technique, the advantage of dynamic machine learning comes from its high probability of spotting zero-day malicious files Xcitium’s dynamic machine learning technique uses hundreds of features extracted from the run-time behavior of a file with the combination of algorithms yielding the best results What We Do for Detection in the Cloud.
Xcitium’s broader machine learning models focus on statistical correlations and trends to identify exploit campaigns and more. Xcitium has than more than 25 static detectors and dynamic detectors that are used as models for statistical correlations with thousands of different features to detect the common features of malware and identify exploit campaigns. Xcitium focuses on machine learning based models designed to accurately identify the rise and fall of exploit campaigns.
We also study trending analyses of exploit submissions by Xcitium’s global installed base and community of independent researchers. This helps us identify campaign attack surface, breadth, geography, industry and other useful metadata to profile and respond to advanced threats.
Embedded Detectors for Analysis
Detectors are a standard function of Valkyrie analysis methods and require no configuration or effort by customers. Xcitium’s embedded detectors are custom script-based detection methods that may be uploaded to Valkyrie to be used and included in final verdicts.
Web Reputation Analysis
Xcitium’s global threat cloud provides the threat intelligence for web reputation analysis tracking different reputation sources to identify about 45 different malicious IP addresses, botnets and C&C servers for example.
Xcitium Valkyrie will analyze files that receive a verdict of malicious, extract the URLs embedded used by the malware and match them against known bad URLs (web reputation blacklist). It also will correlate those bad URLs against all known bad malware to draw associations between polymorphic code, campaigns and threat actors—for reputation by association. Reputation analysis is supported by constant updates and threat intelligence sharing across the enterprise to block malicious domains immediately and alert admins. For example, when a new malicious domain is added to the blacklist, Xcitium Dome Shield at the DNS server consumes the feed. When it gets a traffic request for that domain it blocks automatically and alerts admins. Xcitium Advanced Endpoint Protection is integrated with Dome Shield at the DNS server for immediate protection.
- Domains hosting malware files
- Domains hosting Potentially Unwanted Application (PUA) files
- Domain that send only phishing emails
- Malware connecting to Domains List
- Malware connecting to Domains List
- Malware Command and Control Server Domains
- Domains of drop sites for logs or stolen credentials
- Spyware Reporting Server Domains
- Questionable Gaming Site Domains
- Drive by Source Domains
- Tor Node Domains
- Known compromised or Hostile Domains
- Domains Performing Scanning
- Domains Performing Scanning
- Domains of Fake AV and AS Products
- Domains Related to a Dynamic DNS Entry or Request
- Abused or free TLD Related Domains
- Domains related to Self-Signed SSL or other suspicious encryption
- Blackhole or Sinkhole Domains
- DDoS Source Domains
- IPs that are blacklisted for sending only spam emails
- IPs that don’t have a reverse DNS record
- Malware connecting to IP List
- Malware Command and Control Server IPs
- Known Infected Bot IPs
- IPs of drop sites for logs or stolen credentials
- Spyware Reporting Server IPs
- Questionable Gaming Site IPs
- Drive by Source IPs
- Tor Node IPs
- Known compromised or Hostile IPs
- IPs of Hosts Performing Scanning
- SSH or other brute force IPs
- IPs of Fake AV and AS Products
- IPs Related to a Dynamic DNS Entry or Request
- Abused or free TLD Related IPs
- IPs related to Self-Signed SSL or other suspicious encryption
- IPs of Blackhole or Sinkhole systems
- DDoS Source IPs
- URLs that redirect to malware files
- Final URLs that redirect to phishing files
- Malware connecting to URLs
- Regular expressions of phishing URLs
- URL Patterns that redirect to malware files
- URL Patterns that malware files connect to
FILE LOOKUP SERVICE (FLS) IN THE CLOUD
File Lookup Service (FLS) is a cloud-based application that stores and provides access to information on clients’ requests over standard interfaces. The main task of FLS is to provide the true nature of a file to determine whether it is safe or malware. It also contains information about vendors, file reputations, domain lookup and URL lookup functionalities.
The service’s strength comes from its scalable structure and large capacity to serve billions of client requests per day. FLS eliminates long wait times for analysis of known malware and safe files and continuously updates with new files to ensure customer satisfaction. For example, if a process or executable is not digitally signed as a trusted application or by a trusted publisher, then a SHA1 ‘hash’ or signature will be submitted to the Xcitium Valkyrie FLS. Based on updated global intelligence, FLS will provide an accelerated verdict in case a process or executable is known bad or malware.
The Xcitium Anti-Malware Data Processing Analysis and Management System collects information about different types of files from all around the world. The system processes newly arrived files using legacy methods and stores the results. It also receives analysis results from the Valkyrie file verdict system to validate the true nature of files. This results in a very large data repository in which all the identifying information along with the analysis results and reputation of billions of files is stored.
TRUSTED VENDOR LIST (TVL) IN THE CLOUD
Xcitium Valkyrie extends beyond certificate validation, by incorporating a second control to ensure the security of customers. Xcitium maintains a trusted vendor list (TVL) for this purpose. A file is evaluated as safe if and only if its author is a trusted vendor and its certificate validation is successful.
Certificate validation and TVL checks help to identify safe files quickly and prevent a false malware alarm (false positive) on a clean file Digitally signing executables with certificates helps identify the origin of a file e.g. author and vendor and guarantees that the file has not been corrupted or modified. Digital certificates can be generated by anyone using cryptographic tools.
Therefore, the authorization and authentication plays a critical role and it is important that the issuer of a certificate is globally trusted. Third-party certificate authorities (CAs), such as Xcitium, provide code signing certificates. The trust chain of a CA and operating system is used to validate the authenticity of the file, and the vendor information is extracted. A certificate signing a code may not be directly issued by a CA. However, a certificate of the issuer might be issued by a CA.
This relationship between certificates forms a certificate chain which can be tracked back to a root certificate which is signed by itself. Chain validation checks each certificate in the chain. If none of the certificates has expired, been stolen or revoked, and the root certificate is issued by a trusted CA, then certificate validation is successful. Additionally, a time-stamp check is included to extend code trust beyond the expiration date of a certificate, which means that a certificate may expire but as long as no security incidents are reported, the code can still be trusted.
Related Resources