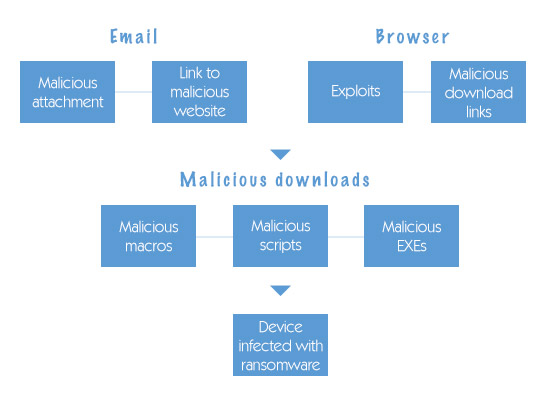
What does a Trojan virus do to your computer?
Updated on October 21, 2022, by Xcitium
What does a Trojan virus do and is a type of malware that is often disguised as a regular file. For example, a Trojan horse virus can appear as a Word document. Trojans are typically used by various cybercriminals and hackers trying to acquire access to an endpoint user’s computer.
Endpoint users are commonly deceived through the form of social engineering such as an email with an infected Word attachment. When the endpoint user opens the document with the Trojan horse virus, the malware loads itself onto the victim’s computer. Once activated, Trojan viruses can enable cybercriminals to spy, steal sensitive data, and gain backdoor access to an endpoint user’s or enterprise’s endpoint system.
While a Trojan performs the same function in that it secretly downloads onto a computer its actions can vary depending on what malware authors have programmed it to do. These actions are wide and varied but some of the most common are listed below.

What does a Trojan virus do: More Things to Know about Trojan Viruses and Cybersecurity
While many people assume that only major businesses such as Amazon, Target, and eBay become victims of cybercrimes, 43 percent of cyber attacks aim at small businesses. A malware Trojan author will not hesitate to attack any endpoint users including small and medium enterprises (SMEs). It is also a fact that 51% of SMEs are not allocating any budget for their cybersecurity. Hence, this makes them the most vulnerable victims to attack. Here are two incidents of what a trojan virus does to its victims:
BackSwap Trojan Horse Virus
Recently, the BackSwap malware attacked six banks in Spain. The trojan virus emerged in March 2018 and only targeted Polish banks. It is most often delivered to users via malware spam. The users will receive an authentic-looking attachment of a productivity file like Microsoft Word or bundled inside other programs. BackSwap poses as a freeware or open-source program and plants its code in the program initialization stage. When the user runs the file during an early stage of the program’s execution, the code replaces the installation routine with malicious instructions that execute BackSwap instead. One interesting choice of code was Ollydbg.exe. It is a program frequently used by malware researchers.
Rakhni Trojan Viruses
In July 2018, Rakhni Trojan viruses were discovered in Russia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Germany, and India. Malware authors distributed this Trojan horse virus mainly through spam mailings with malicious attachments disguised as financial documents. If the user allows editing and tries to open the PDF document, the system asks permission to run an executable file from an unknown publisher. With the endpoint user’s permission, Rakhni starts its operation.
Eventually, the Trojan horse virus shows the victim an error message explaining why nothing has opened. Subsequently, it incapacitates Windows Defender and installs forged digital certificates. Only when the situation appears clear, it decides what to do with the infected device or endpoint. Then, it encrypts files and demands ransom or installs a miner.
What does a Trojan virus do: Xcitium Advanced Endpoint Protection Against Different Trojans
Xcitium has developed systematic procedures to counter what a trojan virus does. They have specific features to combat the threatening qualities of what a trojan virus does. Xcitium Advanced Endpoint Protection provides a lightweight, scalable Default Deny Platform with its one-of-a-kind endpoint security approach, which results in complete protection and enterprise visibility. The enterprise can avoid backdoor trojan definition when they aims to reduce the security vulnerabilities, educate their employees on identifying malicious emails and programs, blocking threats from known malware and exploits. Here are the specific features that help diminish trojan horse viruses:
Machine Learning Through Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning is a vast field of study and research. Xcitium has acquired the latest machine-learning techniques to determine to determine if an unknown file is a trojan horse virus or not.
Xcitium has developed a predictive model that started with collecting a plethora and variety of trojan horse viruses. Features are extracted from files along with the files’ labels (e.g. good or bad). Lastly, the model is inured by feeding all of these features, allowing it to process the numbers and find patterns, and clusters in the data. When the features of a file with an unknown label are presented to the model, it can return a confidence score of how similar these features are to those of the malicious and benign sets. That effectively defends the endpoints from what a trojan virus does. These concepts underpin VirusScope, Xcitium’s file, and the behavioral analysis engine residing on the local client.
A List of Known Trojan Virus files
Xcitium has established its name as its largest brand of certification authorities internationally. Certification authorities issue digital certificates which are used for many purposes. Some of the reasons are for SSL. It is the encryption of confidential information, or digitally signing applications. It allows the operating system to trust the incoming digitally signed application when executing.
Xcitium uses its expertise and knowledge and supplies this into our containment solution as a list of good and safe files.
What does a Trojan virus do Combining Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP) and Endpoint Detection Response (EDR)
Xcitium Advanced Endpoint Protection (AEP) combines both superior prevention with the ability to detect/respond to threats as they emerge. Xcitium AEP goes further in the prevention of threats provided by conventional signature-based detection and AV.
Xcitium AEP includes multiple preventative capabilities including AV, HIPS, ongoing Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning monitoring and layers on the ability to manage and monitor endpoints to quickly resolve issues. Advanced Endpoint Protection provides deep visibility into file activity on your endpoints, detecting malicious behavior that other security solutions may miss, and provides you the control investigate, contain and remediate your entire endpoint environment.
If there will be a case that an unknown, suspicious file will get into the containerization technology, Xcitium AEP can take an action immediately when this happens. It traces any malicious activities that are not supposed to occur while the endpoint environment is in use or during its downtime.
Host Intrusion Prevention System Basic
HIPS represents a preventive approach to network security and utilizes advanced techniques to expose and block attempts to breach an endpoint system. It employs several advanced techniques to scan network traffic and look for patterns in the data. If a possible breach is discovered, HIPS can take several different defensive actions depending on the type and severity of the detected method of a virus and trojan infection. Defensive actions can include alerting the user and/or administrator and automatically dropping suspicious data streams.
Conclusion What does a Trojan virus do
Given the plight of trojan virus attacks on different businesses, it is safer to tighten the cybersecurity. It ensures the smooth operations of the entire enterprise. Choose a smarter and a much more reliable endpoint protection now.
Contact us for more details on how Xcitium AEP can assist your enterprise.
Related Sources: