What Is a Trojan File? — An Analysis
Updated on October 21, 2022, by Xcitium
 Trojan file uses cybercrime and deception to trick unaware users. By running benign PC programs, you can learn to tell what is a trojan file because it hides malicious intentions.
Trojan file uses cybercrime and deception to trick unaware users. By running benign PC programs, you can learn to tell what is a trojan file because it hides malicious intentions.
WHAT IS A TROJAN FILE AND HOW TO DESCRIBE IT?
Consider the trojan virus as an umbrella term for malware delivery. With that in mindt, there are different types of trojan files. Depending on the cybercriminal’s plan, a trojan file acts like independent malware in that it is a tool for different activities. For example, it can communicate with the cybercriminal and deliver malware payloads. At a later time, a trojan file can open up the system to cyberattacks.
To put it another way, a trojan record is a delivery method. Cybercriminals utilize it to deliver any number of threats, such as ransomware to request cash, spyware that disguises itself to require critical data, etc. The trojan horse virus tends to involve money-related and individual information.
Remember that unwanted programs and adware can be mistaken for a trojan file, so it’s delivery strategy is comparable. For instance, sometimes adware sneaks onto your PC as part of a software bundle. You believe that you’re downloading one piece of software, but it’s actually two or three. The program creators usually incorporate the adware for marketing affiliate reasons.
Such adware bundlers are less malicious than the trojan file and do not hide themselves the same way. But since the adware distribution vector looks similar to a trojan file, it can cause disarray.
WHAT IS A TROJAN FILE AND ITS TYPES?
A trojan file is popular and flexible, so it’s hard to describe each type. All things considered, a trojan file is intended to take control of a user’s PC, keep an eye on users, acquire information, or insert more malware on to a user’s PC.
Here are basic threats that can originate from trojan file attacks:
Type #1: Spyware.
It watches as you enter your credit card details or log into online accounts. They then send your passwords and other identifying information back to the cybercriminal.
Type #2: Backdoors.
It creates remote access to your system. This sort of malware changes your security to enable the cybercriminal to steal your information, control the device, and even download more malware.
Type #3: Downloader.
It downloads and deploys different malicious modules, for example, keyloggers and ransomware.
Type #4: Zombies.
It takes control of your PC to make it a slave in a network under the cybercriminal’s control. This is the initial phase in making a botnet, which is often used to perform a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack, designed to bring down a network by flooding it with traffic.
Type #5: Dialer.
This may appear to be out of date since most people don’t use dial-up modems anymore.
WHAT IS A TROJAN FILE AND ITS INFECTION TECHNIQUES?
A trojan file can look like pretty much anything: free music, films, and ads for authentic applications. Any number of hasty user practices can lead to a trojan file infection.
Here are a few examples:
Technique #1: Downloading unknown free programs.
What resembles a free game could be a trojan file, particularly if you discover it on an untrustworthy site.
Technique #2: Downloading cracked applications.
Promises of an illegal free copy of a piece of software can be tempting. But the cracked activation key generator or software may hide a trojan file attack.
Technique #2: Visiting shady sites.
Some sites need a moment to infect your PC. Others use traps, like claiming to stream a well-known movie but only if you download a specific video codec, which is actually a trojan file.
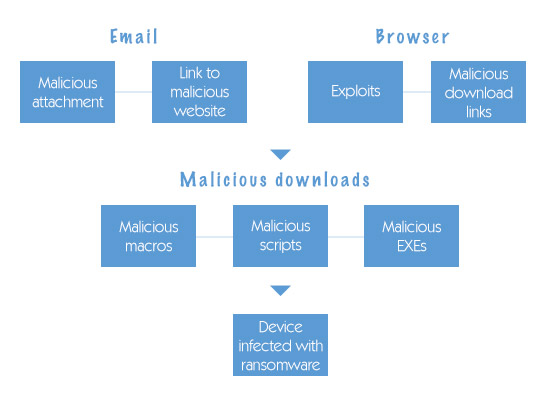
Technique #4: Opening contaminated attachments.
This is when you get an odd email with what resembles an important attachment, but it dispatches a trojan file when you open it.
WHAT IS A TROJAN FILE AND HOW WOULD YOU PREVENT IT?
Since trojans depend on tricking users into giving them access to the PC, most infections are avoidable by staying watchful and observing great security habits. Practice sound skepticism about sites offering free things, opting instead to download free programs from a legitimate site instead of unauthorized mirror servers.
Xcitium Another precautionary measure to consider is to change the default settings so the real extensions of applications are visible. This avoids getting deceived by an innocent-looking icon.
Other great practices besides installing anti-malware software include:
Setting up automatic updates of your OS.
Ensuring that you have the most recent security updates.
Running occasional diagnostic scans.
Keeping your applications updated.
Guaranteeing any security vulnerabilities are patched.
Being suspicious of links and unverified attachments in messages.
Avoiding suspicious or hazardous sites.
Remaining behind a firewall.
Using complicated passwords.
Related Resources